Well, we’ve been waiting for it. Google’s main core algorithm update and spam fighting update have launched. Interestingly, this is the second time they’ve rolled out several updates simultaneously, which significantly complicates SEO specialists’ analysis of the reasons behind a particular site’s decline.
Hi, this is Alex, and this is the new SEO News segment.
Right after launching the update, Google rolled out an explanatory document detailing what it’s doing and what it aims to achieve – one of the points being the fight against drop domains (also known as PBNs). If memory serves, about 7 years ago, Google first cleaned out all the drops and reduced their impact to zero. Let’s see what happens this time.
So:
- The update includes changes to several of Google’s core ranking systems and introduces a new approach to determining content usefulness.
- Google introduced a new spam policy with three new rules: against abuse of expired domains, large-scale content abuse, and website reputation abuse.
- Large-scale content abuse refers to creating large amounts of low-quality, unoriginal content to manipulate rankings.
- Website reputation abuse occurs when third-party pages are placed uncontrolled to manipulate rankings through website signals.
- The update may take up to a month for a full rollout, with possible significant ranking fluctuations.
Thus, the main emphasis is on combating spam and taking a stricter approach to defining useful content to improve search results.
I analyzed the reaction of the webmaster and SEO community to the initial ranking update data. Forums and Twitter saw many complaints from webmasters about site declines or complete removal of their projects from the index.
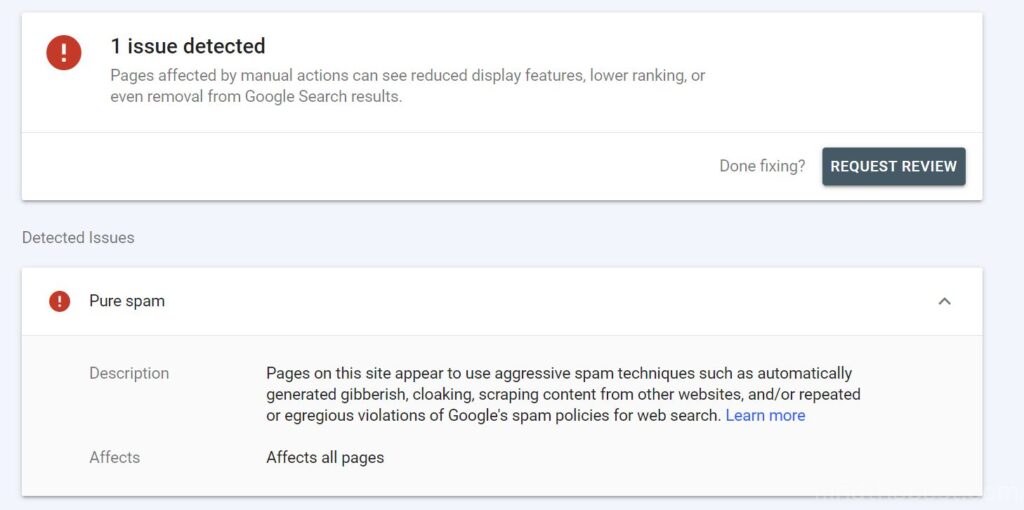
Right after the dual update began, Google started handing out manual penalties and manually deindexing sites. Public Western SEOs who teach creating AI-generated content at scale and practicing parasitic SEO were especially hit hard.
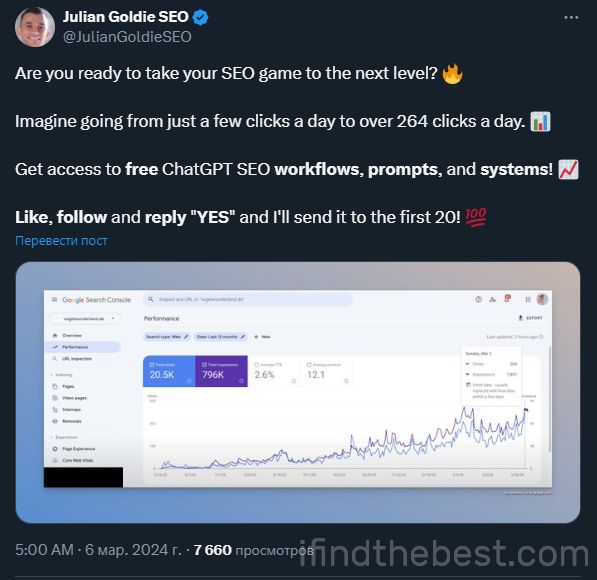
All of Julian Goldie’s public cases were thrown out of the index. As early as March 6, he bragged about the rapid growth of his project. The next day it had already disappeared from the index. His main site received manual penalties.
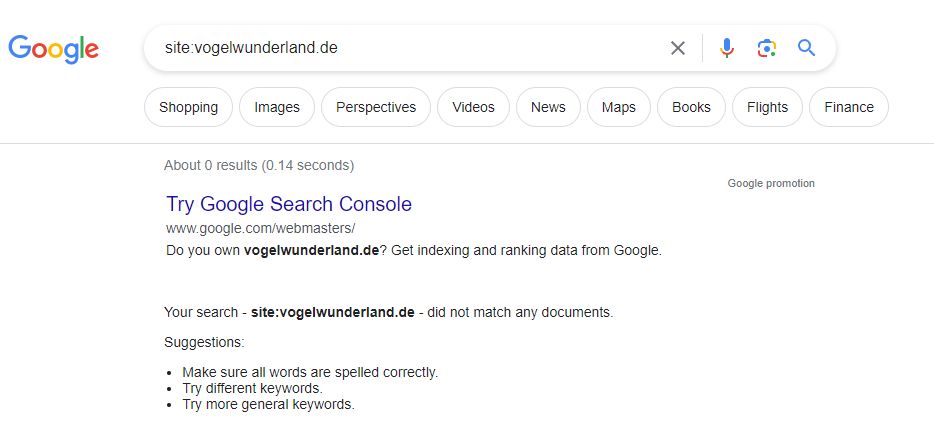
Today it’s already gone from the index 😔
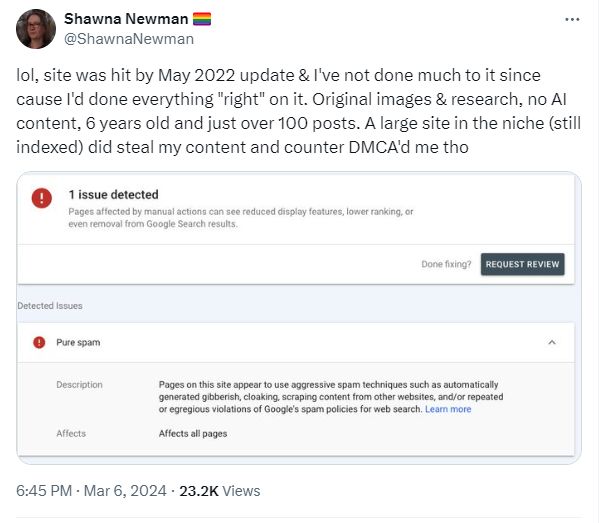
Shawna Newman received manual penalties.
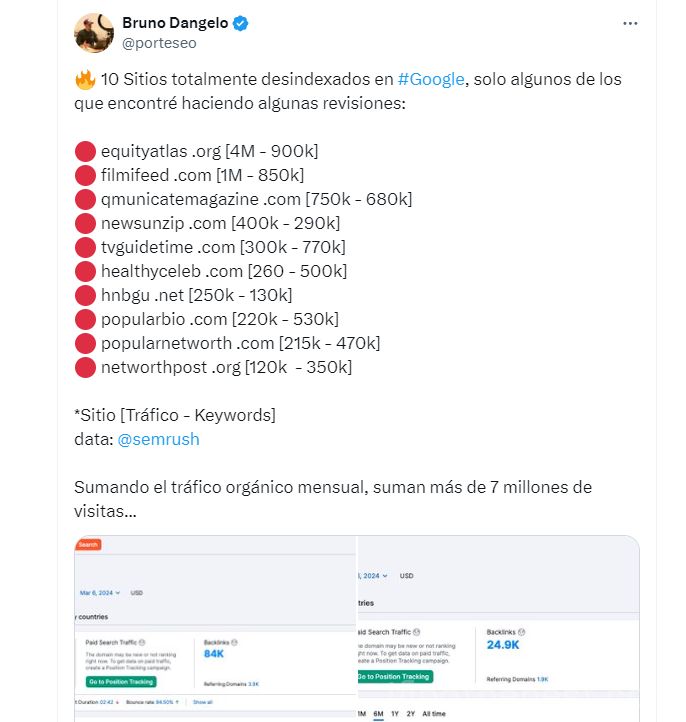
Bruno Dangelo’s 10 traffic sites (up to 1 million visits per month) received manual penalties.

The sites of a well-known affiliate marketer also took a hit. She wasn’t shy about revealing how much income she makes and admitted to using AI for content generation on some of her projects. Although she later claimed the deindexed sites didn’t contain any AI-generated content. All of these sites were under the same Google Search Console account.
Here are some more cases of Google deindexing sites:
- A batch of manual penalties from Charles Floate https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=krj_Mm730_s
- Deindexing of Kashif Riaz’s site with 9 million traffic https://twitter.com/KashifRiazSEO/status/1765336346615537878
- Jackie Chow had all sites in one Google Search Console account hit with manual penalties https://twitter.com/indexsy/status/1765496649093185711
Here https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4sUXiKxMZU4 shows how their revenue went to zero. - Another affiliate site received manual penalties https://twitter.com/SEOarbitrageur/status/1765544821215900149
- Morten Storgaard got manual penalties https://twitter.com/niche_bloggers/status/1765397063460647330
- Chris Miles also had issues https://twitter.com/NicheSiteChris/status/1765547958777377123
So far, it seems the update mainly impacted sites using AI content.
I was amazed when in March 2023, everyone was trashing copywriting and switching en masse to AI. Primarily because it makes no sense. Let’s look at it from the regular user’s perspective:
- Users don’t need sites publishing content copied from ChatGPT or other AI tools;
- Just as they don’t need the most boring rewritten content;
- The popularization of programmatic SEO and AI texts led to a huge number of low-quality sites that overwhelmingly offer very little value;
Logically, Google will fight low quality and look for ways to destroy these trends.
If some new promotion tactic emerges, especially a technology that significantly impacts search quality, Google always improves its algorithms and heavily penalizes sites with high social media exposure. This doesn’t stop the tactic or technology from working, but its impact or effectiveness is discounted, and everything becomes more difficult.
Where are we now? While the scope of the update is still unclear, it’s evident that Google will push the situation toward a more balanced and controlled state. In my humble opinion, this update will bring the trend full circle, where content quality matters, not hundreds of thousands of generated filler content.
I own 5 sites, and so far, I’ve only seen a decline in one project. And on that one, I didn’t use AI content. But the update is still ongoing, so we’ll wait until the end of the month.
Below, I’ve gathered all the useful links regarding Google’s March update:
- You can read more details about the announcement of the core March 2024 update on Google’s blog https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2024/03/core-update-spam-policies
- You can track the start and completion of major updates on Google’s dedicated status panel site https://status.search.google.com/
- If you want to check if your website received a penalty, go to the link below and select the domain you want to check from the dropdown menu at the top left https://search.google.com/search-console/manual-actions
- The “Search Quality Evaluator Guidelines” document was also updated. Specifically, the “Characteristics of Low-Quality Pages” section was updated, and illustrative examples were added https://static.googleusercontent.com/media/guidelines.raterhub.com/en//searchqualityevaluatorguidelines.pdf
If you found this interesting and would like me to provide such an analysis of major SEO and web development news, let me know in the comments.
